A thread is a unit of execution within a program. It allows you to run multiple parts of your program concurrently. This can be useful for tasks that don't require the full attention of the processor, such as downloading a file in the background while the user continues to interact with the application.
There are two main ways to create threads in most programming languages:
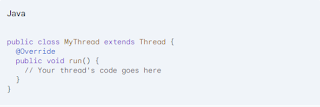
Extending the Thread Class: This approach involves creating a subclass of the Thread class (or its equivalent depending on the language) and overriding the run method. The run method contains the code that the thread will execute. Here's a general outline:
public class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
// Your thread's code goes here
}
}
Implementing the Runnable Interface: This approach involves creating a class that implements theRunnable interface (or its equivalent). The class must also define a run method. You then create a Thread object, passing the Runnable object as a constructor argument. Here's a general outline:public class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
Both approaches achieve the same result: creating a new thread that can run concurrently with the main program. However, there are some advantages to using the Runnable interface:
- More flexible: A class can implement multiple interfaces but can only extend one class. So, using
Runnableallows your class to be more versatile. - Separation of concerns: The
runmethod can be defined in a separate class, making the code more organized. - thread lift up before

No comments:
Post a Comment