Heuristic evaluation is a usability inspection method where experts use established principles, called heuristics, to identify potential usability problems in a user interface (UI). It's a quick and efficient way to find major usability issues early in the design process, saving time and resources compared to full-blown usability testing.
Key principles of Heuristic Evaluation:
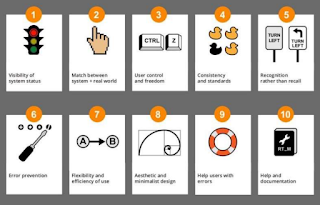
Jakob Nielsen, a renowned usability expert, developed 10 principles of heuristic evaluation that are widely used and adapted in various contexts:
- Visibility of system status: The system should always keep users informed about what is happening, through appropriate feedback within a reasonable time.
- Match between system and the real world: The system should speak the users' language, with words, phrases, and concepts familiar to them, rather than system-oriented terms.
- User control and freedom: Users should have the freedom to easily undo and redo actions, and have clear exits out of unwanted states.
- Consistency and standards: The system should follow platform and industry conventions for consistency in layout, terminology, and behavior.
- Error prevention: The system should be designed to prevent errors or gracefully handle them when they occur.
- Recognition rather than recall: Minimize the need for users to remember information across different parts of the interface.
- Flexibility and efficiency of use: Cater to different user skill levels and allow for customization to match individual preferences.
- Aesthetic and minimalist design: Interfaces should be visually appealing and use clear, concise language, avoiding unnecessary clutter.
- Help users recognize, diagnose, and recover from errors: Error messages should be clear and constructive, guiding users towards solutions.
- Help and documentation: Provide easy access to help and documentation that is relevant, specific, and searchable.
Benefits of Heuristic Evaluation:
- Cost-effective: Requires fewer resources compared to full usability testing.
- Early identification of issues: Catches usability problems early in the design process, saving time and money.
- Focuses on expert knowledge: Leverages the expertise of evaluators to identify potential usability problems.
- Complements other methods: Can be used alongside other usability testing methods for a more comprehensive evaluation.

No comments:
Post a Comment